2.1 Introduction
Buses constitute a very important part of ground transport in Norway and in some cases on international level. In a survey from The Norwegian Directorate for Children, Youth and Family Affairs (Bufdir) report “Use of public transport in the population and among persons with disabilities from 2017, it is shown that buses are among the most used means of transport for many groups of persons with disabilities (besides private cars).
Table 5: How often do you normally use the following means of transport? Number who have answered daily/weekly. Percentage.
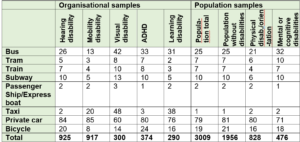
Figure 1 Table on the use of different means of transport used by categories of disabilities (Sourse: Bufdir: Bruk av kollektivtransport i befolkningen og blant personer med nedsatt funksjonsevne (rapport 2017))
The same report also addresses the particular challenges the different groups have with using buses and the reason for not choosing bus transport:
- Persons without disabilities: it takes too long (52%), departure times (38%, expensive mode of travel (27%).
- People with hearing impairments: Same as above (38%, 34% and 19%), respectively, but in addition: poor information during the journey or difficulties with communication or with other social situations.
- Persons with reduced mobility: difficulties with boarding and disembarking (57%), difficulty getting to a stop (37%) or long distance to a stop (37%), conditions at the stop (27%), poor winter maintenance (27%) and lack of assistance from the driver (19%).
- Blind and visually impaired persons: Difficulty stopping the right bus (14%), difficult to find information in advance of travel (9%), difficult to get on and off bus (8%). Other causes (such as visual impairment in general) account for 56%.
- People with ADHD: Uncomfortable with many impressions (39%), it takes a long time (33%), or difficulties related to predictability, price, information on departure times, ticket purchases and route information, communication or social situations.
- People with intellectual disabilities: Difficulties with communication or social situations (52%), uncomfortable with many impressions (24%) or technical challenges with ticket purchases and route information (21%).
2.2 Embarking and disembarking
2.2.1 Legal requirements
For road transport the following legislation applies:
- Act on Occupational transport with engine and vessel (the professional transport law) (Lov om yrkestransport med motorvogn og fartøy (yrkestransportlova)
The Occupational Transport Act entered into force 2003-01-01 and does not have provisions on universal design or, but is required in connection with the transport of persons with disabilities.
- Act relating to amendments to the Occupational Transport Act (implementation of EEA rules on bus passenger rights)
The act entered into force 2015-01-01. The Act introduces a new section 32a on passenger rights to the Occupational Transport Act, which, among other things, affects passengers with disabilities; namely, that the Ministry of Transport and Communications can point out bus terminals that are intended to offer assistance for persons with disabilities, and provide regulations on such schemes.
Comment: This law addresses demands for adaptation, not universal design.
- Regulation relating to universal design of motor vehicles in mandatory transport, etc.
This Regulation of 2009 is pursuant to the Act relating to commercial transport by motor vehicle and vessel (Occupational Transport Act). The Regulation entered into force in 2010-01-01. The Regulation covers scheduled passenger transport, with buses in classes II and III as well as for scheduled transport for persons with disabilities (i.e. motor vehicles specially designed with regard to transport for persons with disabilities). The rules include requirements for approval of the vehicles.
- Regulation, technical requirements and approval of vehicles, parts and equipment (Vehicle Regulations)
The Regulation entered into force 1997-01-01 and were last amended in 2015. It is pursuant to the Road Traffic Act.
The Regulation does not refer to universal design but have provisions that apply to passengers with disabilities.
The Regulation entered into force 2016-04-01 and is an implementation of EU Regulation (EU) No 181/2011 in Norwegian law. The following provisions are relevant:
- 3. Participation for organizations representing persons with disabilities or reduced mobility states that:
“The Norwegian Public Roads Administration shall take the initiative to appoint a group in accordance with Regulation (EU) No. 181/2011 Article 11”.
- 4. Designation of bus terminals to offer assistance to persons with disabilities or reduced mobility states that:
“The Norwegian Road Directorate points out bus terminals that are intended to offer free assistance to travellers with disabilities or reduced mobility. The designation is made by individual decision”.
- EU legislation
- Directive 2001/85/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 20 November 2001 relating to special provisions for vehicles used for the carriage of passengers comprising more than eight seats in addition to the driver’s seat, and amending Directives 70/156/EEC and 97/27/EC
The Buses and Coaches Directive [i] entered into force in the EU in 2001 and in Norway on 13 February 2004. [ii]
The directive sets requirements for Class 1 buses, city buses. Class 2 buses (suburban buses) and Class 3 (express buses) are not included. It is up to the Member States themselves to set requirements for Class 2 and Class 3, in which cases technical specifications shall be used as already stated in the Directive. The Commission has previously in a memorandum requested that it be able to make new directives for commercial vehicles before 2010, without any further specific information.
The Bus Directive sets specific requirements for the design of the buses that essentially benefit the disabled. The requirements are set out in Annex VII” Requirements for Technical Devices Facilitating Access for Passengers with Reduced Mobility”, and include, among other things,
- priority seating for passengers with reduced mobility, including that at least one such seat should have space under or next to it, for a guide dog;
- communication equipment;
- pictograms, which should be clear and located outside the bus so that it is clearly seen which entrance is available for wheelchairs;
- requirements for spaces for wheelchairs;
- installation of folding seats in the place where wheelchairs can be attached;
- attachment for wheelchairs;
- illumination at the boarding and disembarking points for people with reduced mobility, as well as
- directives for various boarding aids, including the kneeling system for the bus, lift and ramp.
- Regulation (EU) No 181/2011 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 February 2011 concerning the rights of passengers in bus and coach transport and amending Regulation (EC) No 2006/2004 Text with EEA relevance
The Regulation entered into force in 2011 and addresses rights for passengers with disabilities.
Appendix I Assistance to disabled and mobility impaired persons addresses several topics:
- assistance at designated bus terminals;
- the possibility of passengers with disabilities being able to report arrival at the terminal and the need for assistance;
- assistance in order for passengers to move from the meeting point to the check-in desk, waiting area and departure area; for boarding, placement of baggage, baggage collection and disembarkation;
- assistance in the bus, including information, boarding and disembarking if there are other personnel than the driver on board the bus, etc.
Appendix 2 The handicap related education addresses requirements for training personnel on such bus routes.
Comment: This Regulation addresses requirements for adaptation, not universal design.
[i] Direktiv Dir 2001/85/EC
[ii] http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2002:042:0001:0102:DA:PDF

